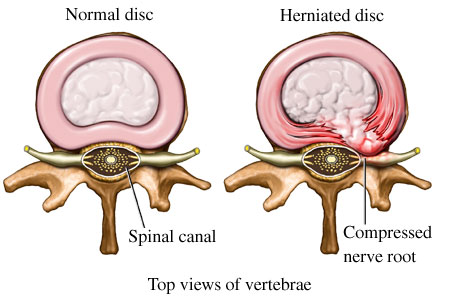
Herniated disc is a condition affecting the spine, in which rupture of the outer annulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc allows the nucleus pulposus to deform and to get out. Herniated disc can be obtained on each disk in the spine, but the two most common forms are cervical disc herniation and lumbar disc herniation. Herniated disc are usually the result of wear and tear, such as frequent work in a sitting position, but mostly at hard labor with frequent heavy lifting.
Symptoms of Herniated disc:
- Acute low back pain;
- Pain radiating to the buttocks, leg and foot;
- Amplified pain when coughing, straining, or laughing;
- Tingling, numbness of the leg or foot;
- Weakness or atrophy ( in later steps ) of the muscles of the legs;
- Muscle spasms.
Cervical ( neck ) disc herniation
- Acute low back pain;
- Neck pain, especially back and sides;
- Deep pain near or over the shoulder blade of the relevant side;
- Pain radiating to the shoulder , forearm , hand and less wrist , fingers or chest;
- Pain is amplified when coughing, straining , or laughing;
- Gain pain tilting or turning the head in various sides;
- Spasm of the neck muscles;
- Weakness of the muscles of the hand.
Diagnosis of Herniated disc:
Imaging:
- Sciagraphy
- Computed tomography (CT, CT) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)
- Myelogram
- Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction study
Treatment of Herniated disc:
- Bed rest;
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs);
- Physiotherapy;
- Oral steroids (e.g., prednisone or methylprednisolone);
- Epidural injection of corticosteroid;
- Weight control.