Kinesitherapy is treatment through movement or therapeutic gymnastics. This is an area of exercise-based physiotherapy. Movement in this case is a remedy that affects the condition of the whole organism. The most important task of kinesitherapy is the elimination of physical impairment and preparing the patient for further rehabilitation, such as social.
Kinesitherapy is used for prevention, rehabilitation and recreation. The exercises are selected individually according to the needs of the patient. The main indications for the use of kinesitherapy are:
● diseases and dysfunctions of the musculoskeletal system – fractures, amputations of limbs, paresis, joint degeneration,
● back pain and posture defects
● rheumatic diseases,
● diseases of the nervous system – Parkinson’s disease, damage to the periphery of the nervous system, multiple sclerosis,
● diseases of the respiratory system – the presence of atelectasis, pneumothorax,
● cardiovascular diseases – myocardial infarction, stroke, hypertension, coronary artery disease,
● pregnancy – kinesitherapy used in preparation for childbirth,
● obesity.
Kinesitherapy is divided into local and general. The local is based on direct impact on the damaged organ, while the general includes exercises on parts of the body that are not affected by the disease. General kinesitherapy is designed to improve the overall physical condition and efficiency of the body. Exercises in kinesitherapy are selected individually – depending on the patient’s problems and the goals he wants to achieve.
In kinesitherapy there are:
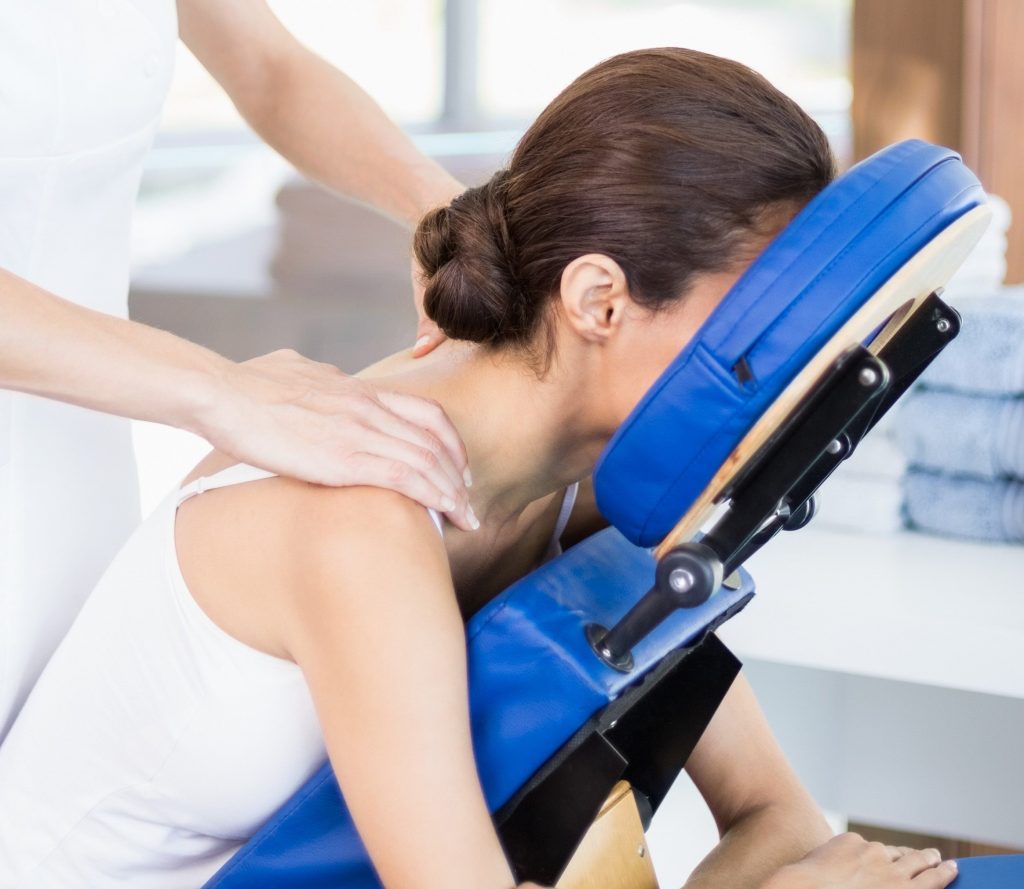
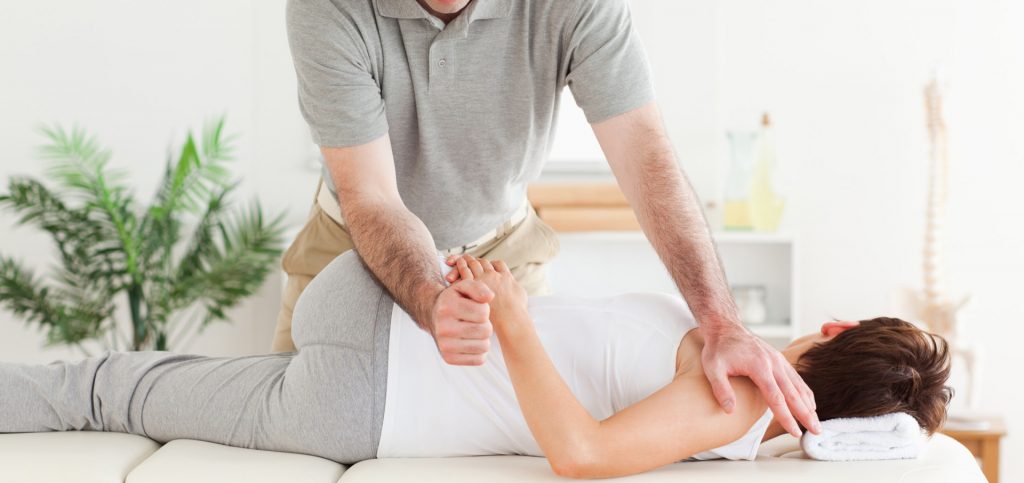
● passive exercises – the patient’s limbs are moved appropriately by a therapist or a special device, the exercises are used in people with muscle paresis, paralysis, long immobility,
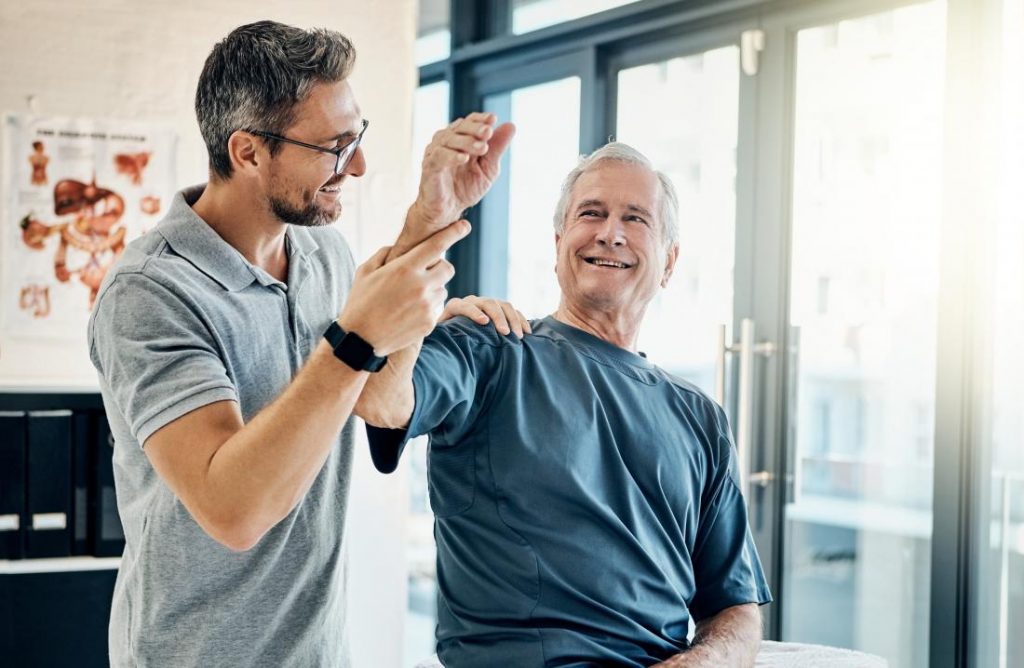
● active-passive exercises – the patient cooperates with the therapist; the latter performs movement, and the former must relax the muscles, exercise is useful after surgery and in degenerative diseases,
● active exercises – they are performed by the patient, alone or under the supervision of a physiotherapist, the exercises can develop motor memory and the speed of reaction of movement stimuli,
● resistance exercises,
● relieving exercises – the exercised part of the body is relieved to facilitate the work of the therapist,
● isometric exercises – involve tightening the muscles without changing their length, ie. without limb movement, exercise helps to strengthen muscle strength and endurance,
● breathing exercises – they should teach the patient to breathe properly and increase lung capacity, which affects the degree of oxygenation of the blood,
● relaxing exercises,
● self-supporting exercises – the patient with the strength of the muscles of a healthy limb supports the movement of a sick patient, the exercises help to increase the mobility of the joints,
● exercises with suspension – the limbs are placed in special brackets hung on ropes. However, the patient moves them alone, the exercises are suitable for people with muscle weakness or atrophy.
Exercises in kinesitherapy should be performed in accordance with the natural anatomy of the human body, ie. the movements in the joints during the exercises must be in accordance with their physiological axis. It is also important for the patient to consciously relax their muscles to reduce overall body tension.